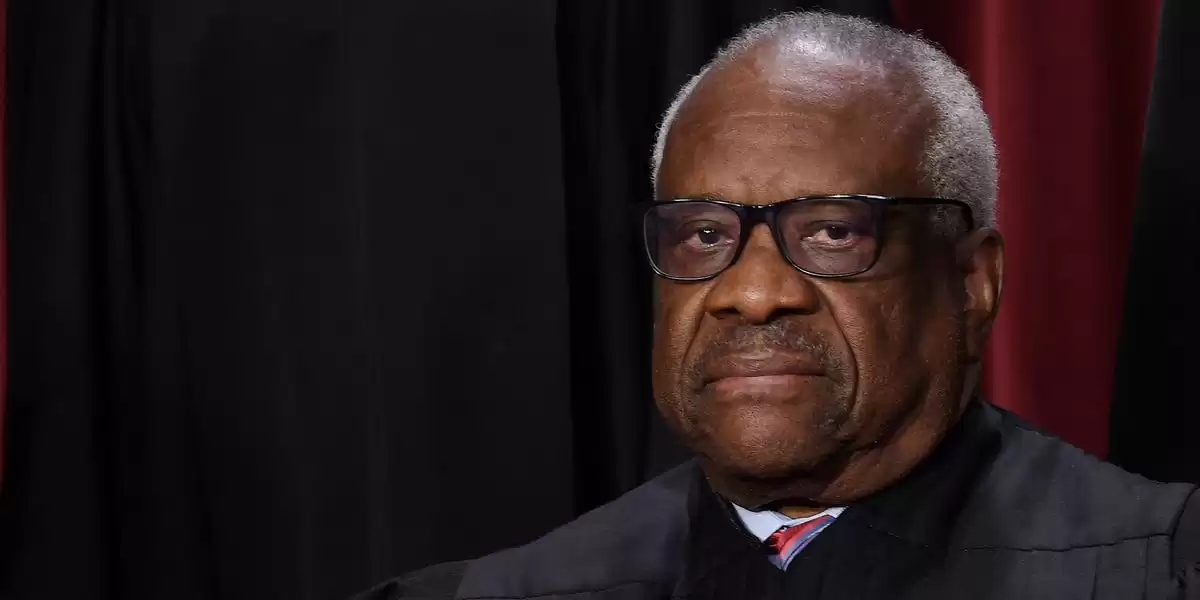
Clarence Thomas acknowledges the adverse impact of social and economic challenges on his community while ruling against affirmative action.
Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas believes affirmative action is unconstitutional.
Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas delivered a powerful opinion as the Supreme Court made a significant ruling on the issue of affirmative action in US colleges and universities. In a 6-3 decision, the court declared that the policies at Harvard University and the University of North Carolina were unconstitutional, effectively outlawing affirmative action.
Thomas, who is the second Black justice to be appointed to the Supreme Court, began his opinion by acknowledging the challenges faced by Black people in the United States. He expressed his hope that the country would uphold the principles outlined in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution, emphasizing the importance of equality and equal treatment under the law.
Asserting that "the Constitution prevails," Thomas argued that affirmative action policies amounted to discrimination. He described them as "rudderless, race-based preferences designed to ensure a particular racial mix" in the entering classes of Harvard and UNC. According to Thomas, these policies directly contradicted the colorblind nature of the Constitution and the nation's ideal of equality.
While Thomas found support from his conservative colleague, Justice Neil Gorsuch, who criticized the role of "bureaucrats" in his own opinion, liberal justices strongly opposed the ruling. Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson, the other Black justice on the Supreme Court, expressed her dissent by calling out her colleagues' "let-them-eat-cake obliviousness." She argued that disregarding race in law did not erase its significance in everyday life.
This decision marks a significant moment in the ongoing debate surrounding affirmative action. The Supreme Court's ruling has sparked intense discussions about the constitutionality of race-based preferences in college admissions and the broader implications for achieving equality in the United States.










Comments on Clarence Thomas acknowledges the adverse impact of social and economic challenges on his community while ruling against affirmative action.